Lessons on building a viral consumer app: The story of Saturn
How single-player utility, hyper-personalization, doing things unscalably, and thinking long-term helped us bootstrap a brand-new social network
👋 Hey, I’m Lenny and welcome to a 🔒 subscriber-only edition 🔒 of my weekly newsletter. Each week I tackle reader questions about building product, driving growth, and accelerating your career.
P.S. Don’t miss Lennybot, my AI chatbot that’s trained on every newsletter post and podcast interview.
I recently heard about an app called Saturn that reached the top of the App Store charts—and stayed there. This is incredibly rare. As I dug in and chatted with the founders, I was blown away by how methodically they were able to articulate what it takes to build a viral consumer app (particularly one targeted at Gen Z). They launched the company back in 2019, while still students at the University of Pennsylvania, and today have scaled the app to millions of users and nearly 20,000 schools.
Their cap table is also unreal and includes General Catalyst, Insight, Coatue, Dick Costolo and Adam Bain’s 01 Advisors, and folks like Marc Benioff (CEO and co-founder of Salesforce), Dara Khosrowshahi (CEO of Uber), Ashton Kutcher, Robert Downey Jr., Mike Vernal (Sequoia), Bezos Expeditions (the personal investment company of Jeff Bezos), Elad Gil, and Dylan Field (CEO and co-founder of Figma). I’m not an investor, but I wish I were.
Below, co-founders Dylan Diamond and Max Baron share their biggest lessons on building a viral social consumer app, including:
Embracing single-player mode as a wedge for social products
Building a product that users feel was built just for them
Why it’s OK to be unscalable—you can make it scale later
Building a familiar product is much easier if you’re solving a problem you’ve experienced
Playing the long game
I spend most of my time looking for patterns across many successful companies, but often you can learn more by studying a single example in depth. This is an excellent example of the latter.
For more on Saturn, check out joinsaturn.com.
Saturn is a social network built around the calendar. We started in high schools by building the most powerful real-time calendar ever made exclusively for students. Today we support millions of students at nearly 20,000 schools across the country, entirely bottom-up through the students themselves, without a single school partnership.
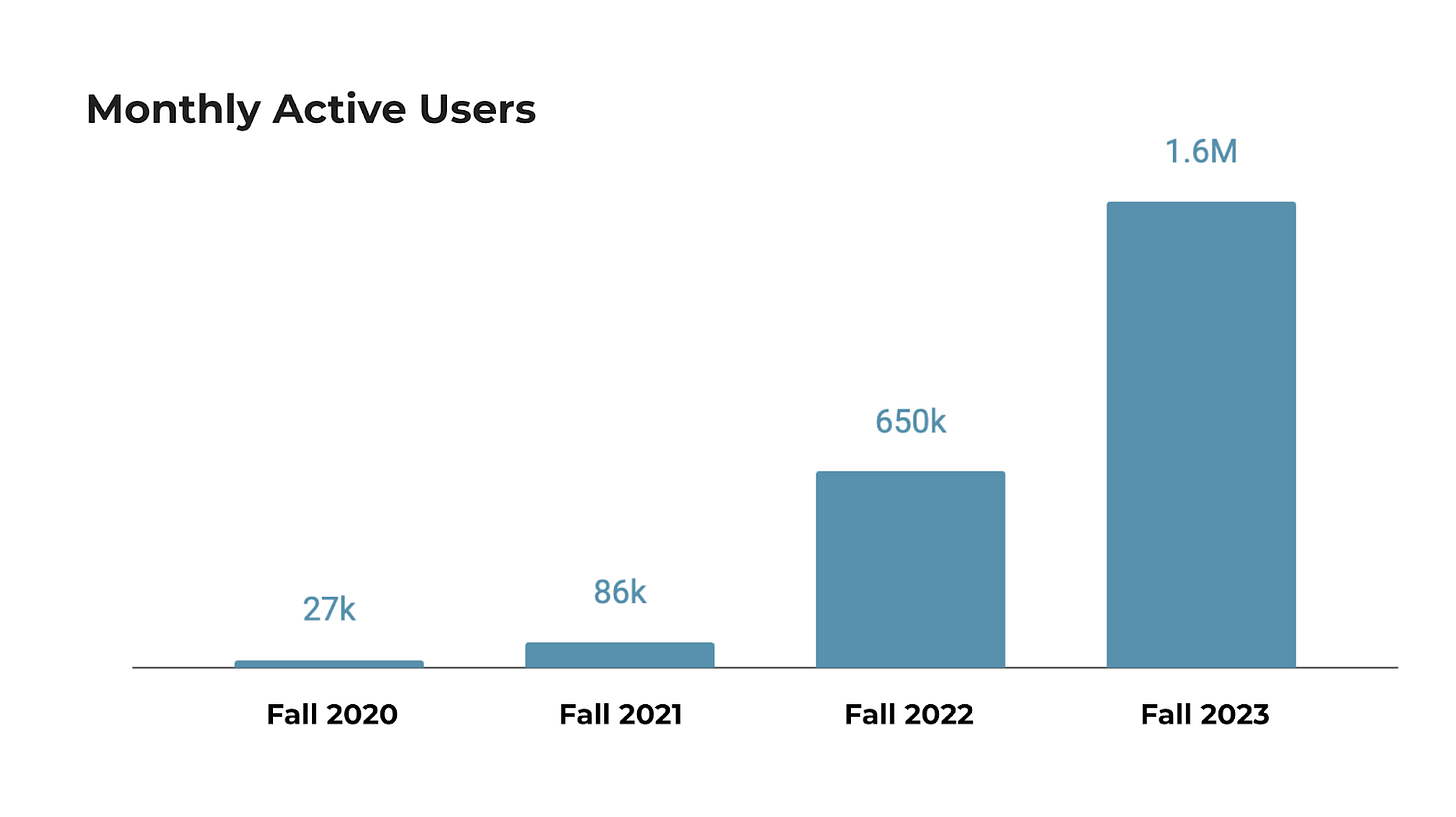
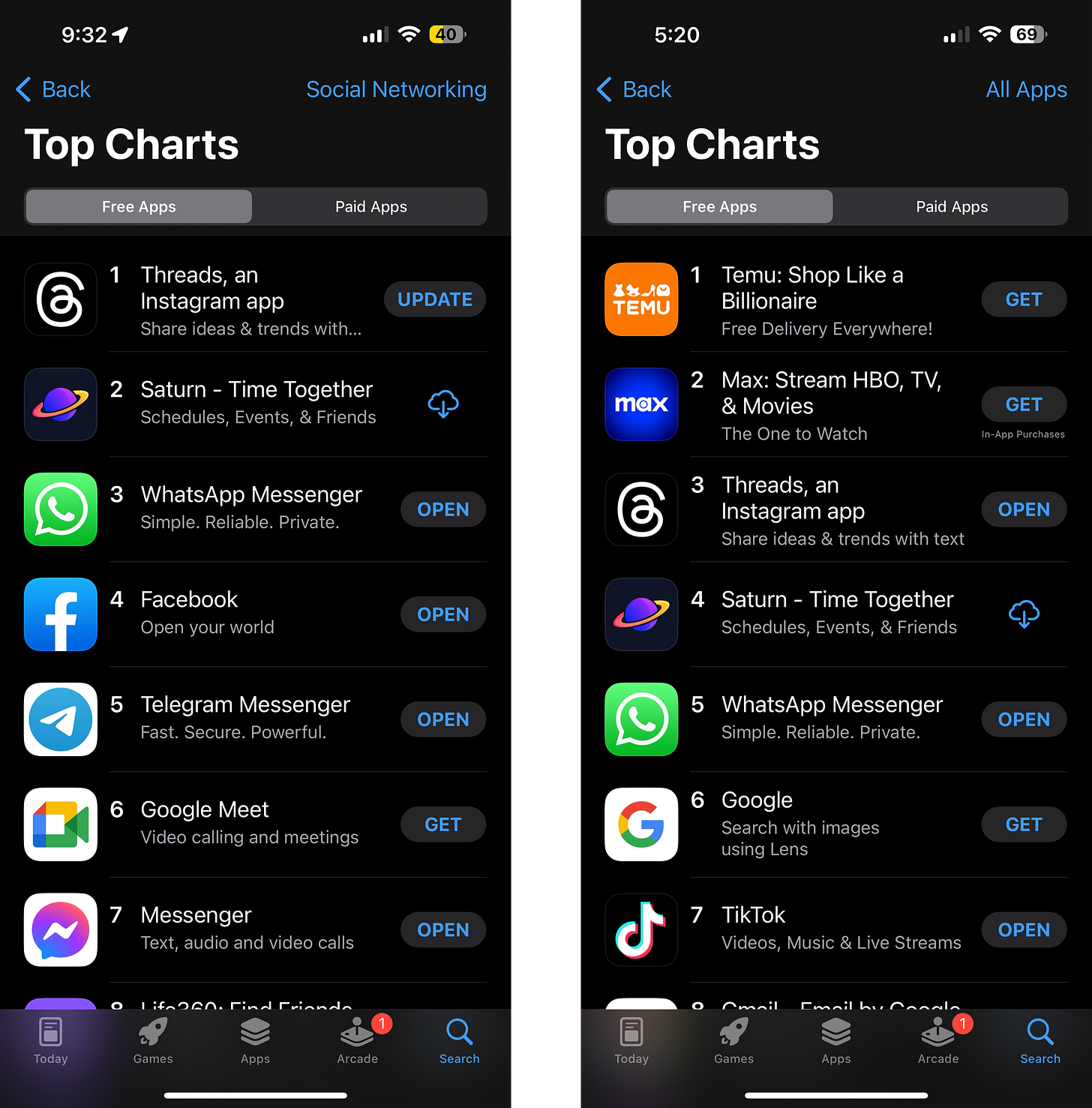
It took years to build critical mass by launching at enough schools to see a significant inflection in our growth and the development of real network effects. This August, we reached fourth overall in Apple’s App Store and second on the Social Networking charts, while maintaining a tailored and closed network for each school.
We have a long way to go and millions more students to support, but here are a few lessons we’ve learned that might be useful in building your own consumer social product.
Quick note/disclaimer: No two apps, or growth journeys, are going to be exactly the same—so these lessons won’t be directly interchangeable, but hopefully you can draw from some of them in making your own product and go-to-market decisions. We also note some of the (many) lessons we’ve learned from other major social networks and social utilities since getting started ourselves in 2019.
1. Embrace a single-player mode as a wedge for social products
Many people talk about the value of a “single-player mode.” The reason is simple: it usually unlocks retention, and retention unlocks time—time to iterate and improve on your product. In our case, having a single-player mode gave us more time to launch and refine key social features that improved the network effects of our product. Great retention reduces the cost of making mistakes, and allows you to take bigger risks and learn faster.
Chris Dixon wrote about this in a 2015 piece called “Come for the tool, stay for the network,” observing that “starting a network from scratch is very hard. Think of single-player tools as kindling.”
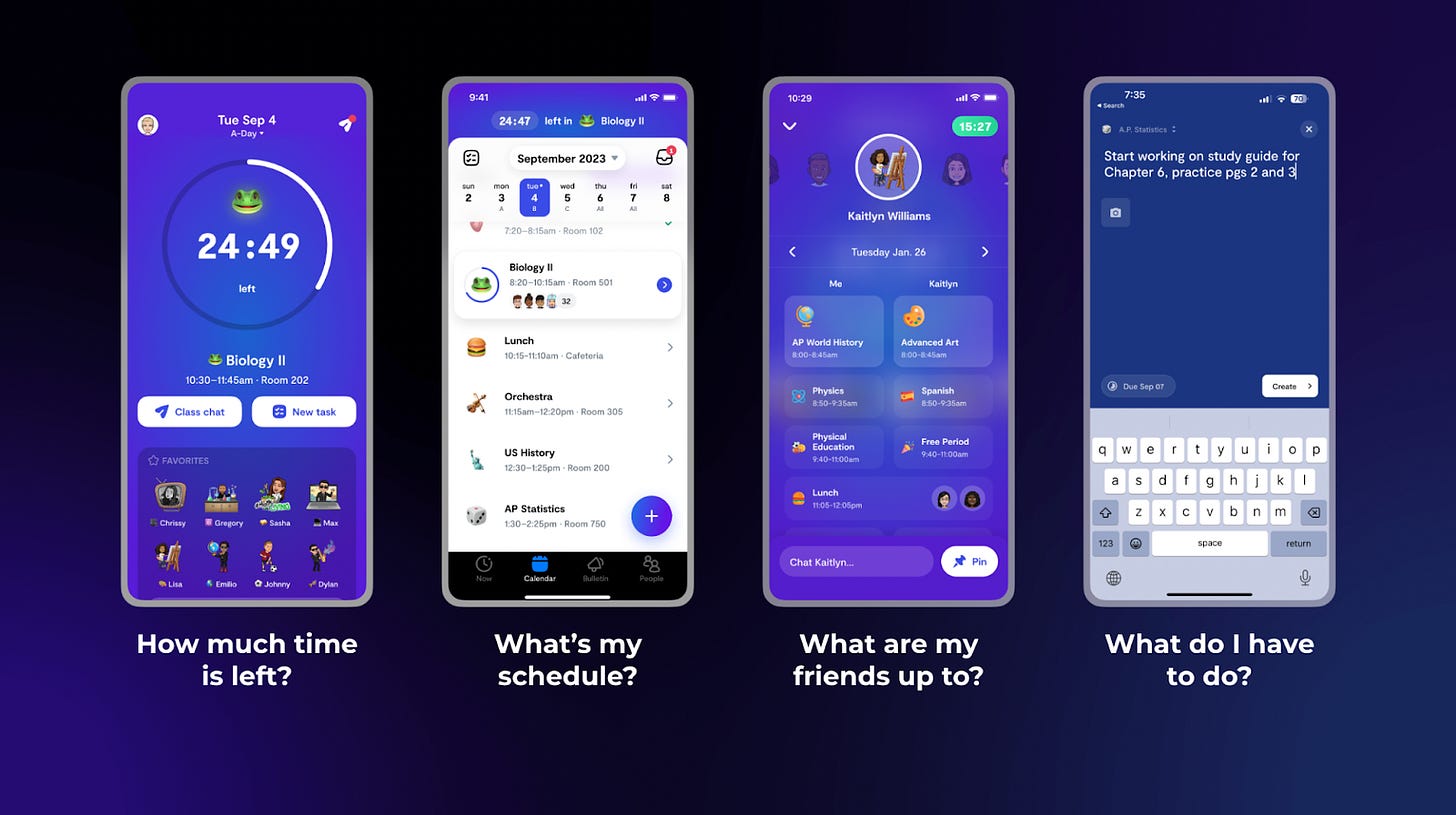
From the beginning, Saturn combined a (primary) single-player utility as a user’s daily calendar with a multiplayer or “social” value that came from being able to see what your friends were doing during the high school day. Over time, we’ve introduced new utility and social use cases and continue to invest in those, but our retentive hook has remained a calendar, originally single-player, eventually multiplayer, that perfectly supports each school.
Since we started Saturn, many apps have achieved “hypergrowth” in various demographics with novel multiplayer social features and more impressive K-factors than ours, but, without a retentive single-player utility, most of them seem to have experienced a destructive inverse K-factor as well. As your friends start leaving, the product quickly gets significantly worse. That decay in value is nonlinear. Early departures disproportionally worsen the overall value of the network.
Here’s an example of how this happens: A new app is super-popular. All of your friends are posting to it once a day. Over the course of a weekend, three of those friends don’t post—it’s not a coordinated effort, but they just aren’t motivated by the notification loops and existing content. Suddenly the library of available (and relevant) content has been significantly reduced, and the product as a whole has become significantly less compelling. Over the coming days, another three people open the app, just to check in, but don’t feel like they need to post. In the span of just a few days, you’ve lost 60% of your creators, and for those final four users, the product is a shell of what it was just a few days before.
When the value of an app is almost entirely social, any change in the network will have outsized effects on its overall health. When a network starts shrinking, things spiral quickly, and when a few of your friends stop creating or participating, there is less of a pull for you to participate.
These are products with great social loops but lack a legitimate single-player use case that keeps you coming back. This rarely works out. You want to build a product where users can survive in smaller pockets—or, better still, alone. Saturn works well even if you are alone, since our calendar provides single-player value and helps you manage your schedule, regardless of how many others may be on the platform. This shows in our new-user retention across the whole platform:
For context on D30 retention, all of Snap, TikTok, Twitter, and Facebook have D30 new-user retention between 28% and 40% (source). Ours is currently in the mid-30s.
It’s important to note that there are social products that have built single-player utility after they built a network, and others, like Facebook, that never had to.
But many did. For example, Venmo didn’t start as a social payment network with a robust activity page; it had a clear utility-based user story that was deeply valuable to you: “get paid by a friend.” Of course, over time, as the network formed, they developed a significant moat and a network effect that resulted in the story changing to “get paid by your friends—all of them—even faster.” There was a very clear utility-oriented use case along the entire journey—and one that helped them survive within friend groups, even if it didn’t work initially between them.
Takeaway: Look for (and double down on) a single-player use case to increase retention (both short- and long-term) that will help unlock time to figure out multiplayer social features that create lasting network effects.
2. Build a product that users feel was built just for them
Most experiences on your phone feel remarkably impersonal. From day one, our approach helped make Saturn a refreshingly personal experience.
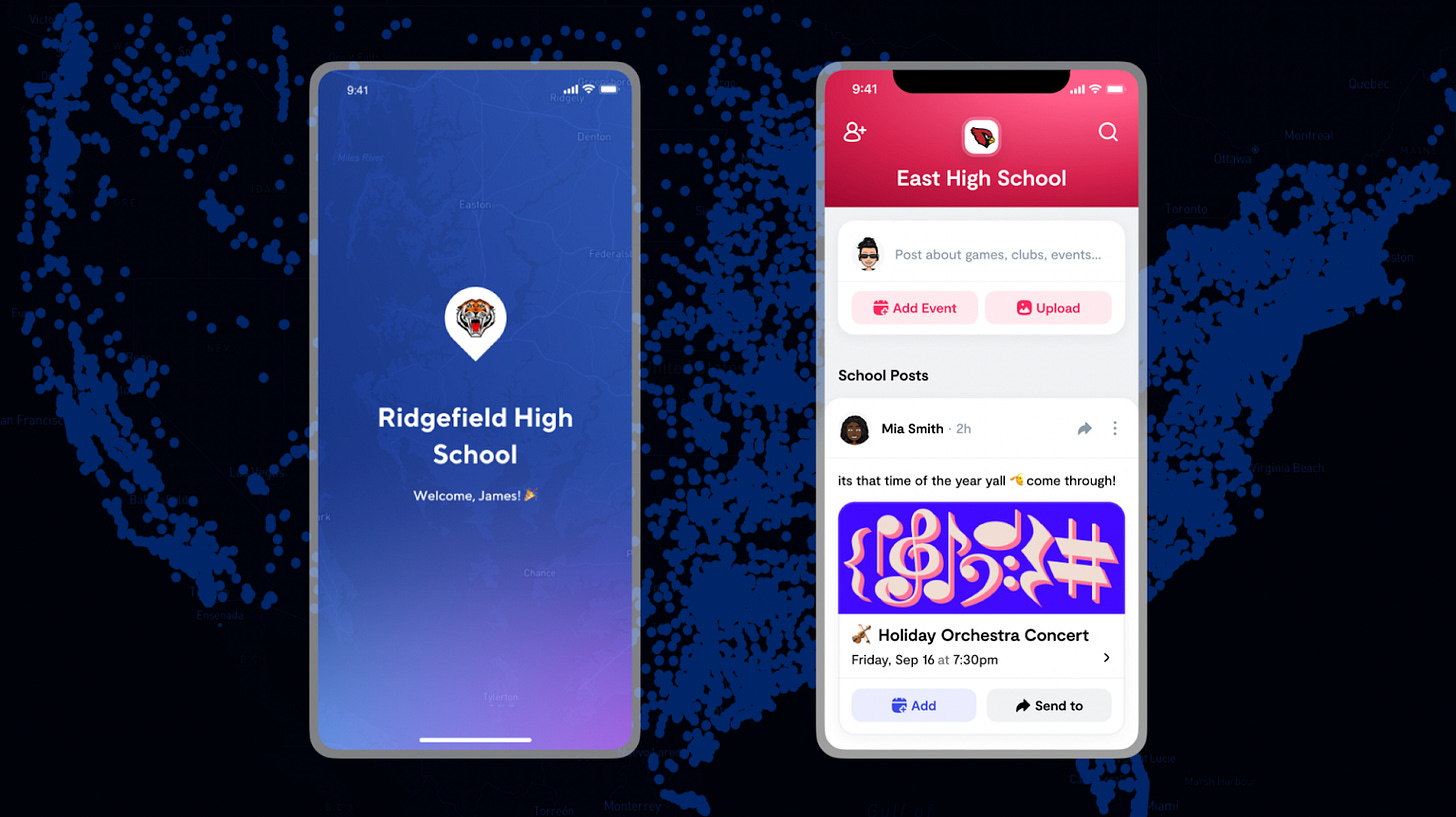
We started by white-labeling an app for the students at Connecticut’s Weston High School. We spent a month working with our student ambassador there to deeply understand the complexities of her schedule and the challenges it resulted in for her and her friends. Then we built iWeston to perfectly support their calendar.
The night we launched, more than half of the student body joined in just the first three hours.
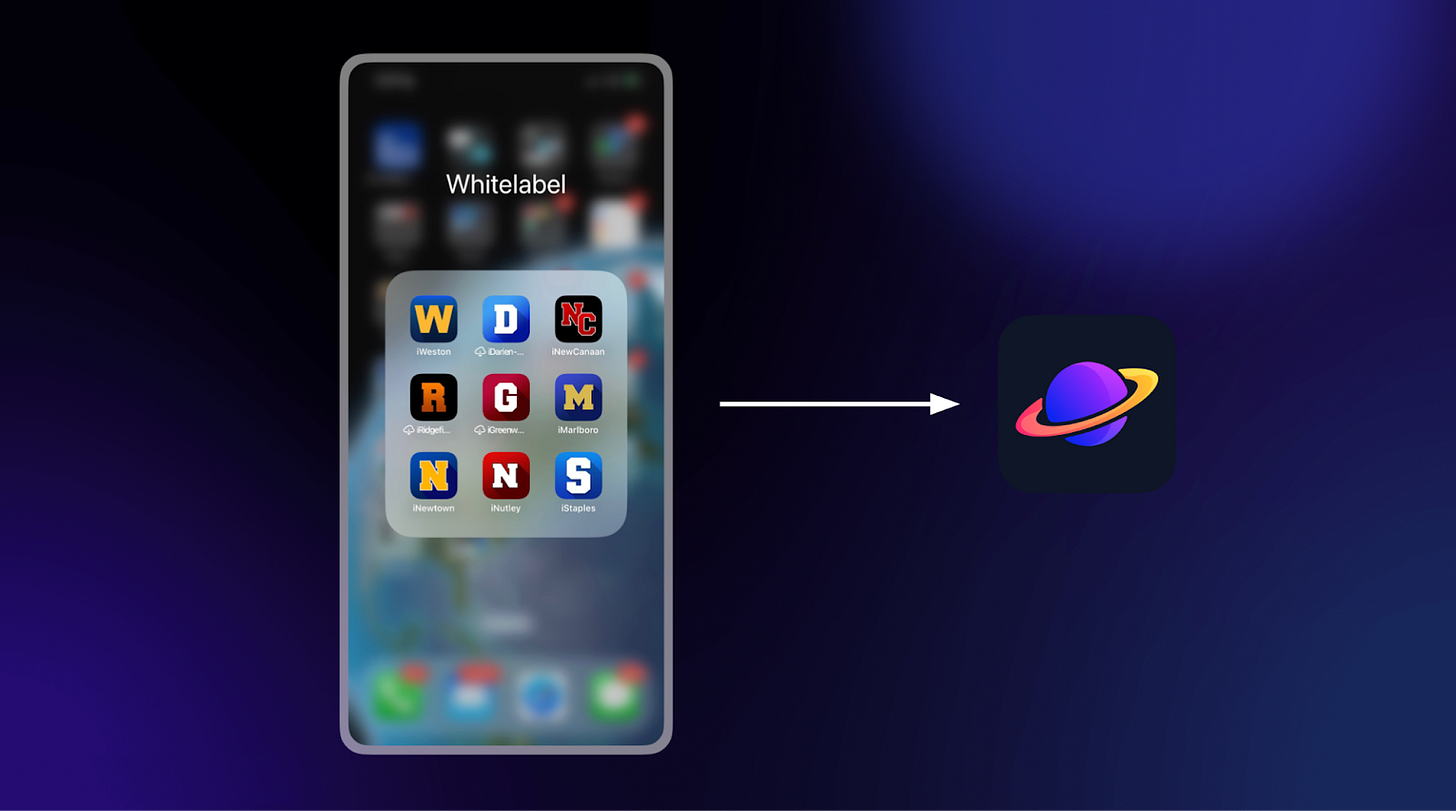
For our first 17 schools, we repeated this process of launching white-labeled apps, each with the school’s letter as its icon, making the app more recognizable and reducing friction to download on the App Store. Another benefit: it looked better on users’ home screens.
When you logged in to any of these apps, you were greeted with an experience that was colorized for your school and perfectly supported the complexities of your schedule. It felt like the app had been built just for your school, because it was.
These school launches were really exciting. We’d recruit an ambassador and then work with them to understand the mechanics of their school, which took less time as we became more familiar with complex schedules. We’d then work with them to spread the word on “launch night” and in the days that followed. They were consistently excited to launch at their schools, and frequently earned social capital for having been our ambassador. For the first few launches, growing at a school was as simple as orchestrating Facebook posts in school-related groups and texts in group chats to help make sure people knew the app was available. Over time, we honed this process, adding sharing links, developing custom landing pages, and adding dynamic content that could be shared directly to your social stories—all of this with the goal of making it easier to invite your friends to join you.
By virtue of this product and growth strategy, we came to market with an experience that was unusually perfectly fit to the audience of a specific school. This translated into incredibly fast adoption at schools. It was common to win a critical mass at schools in hours:
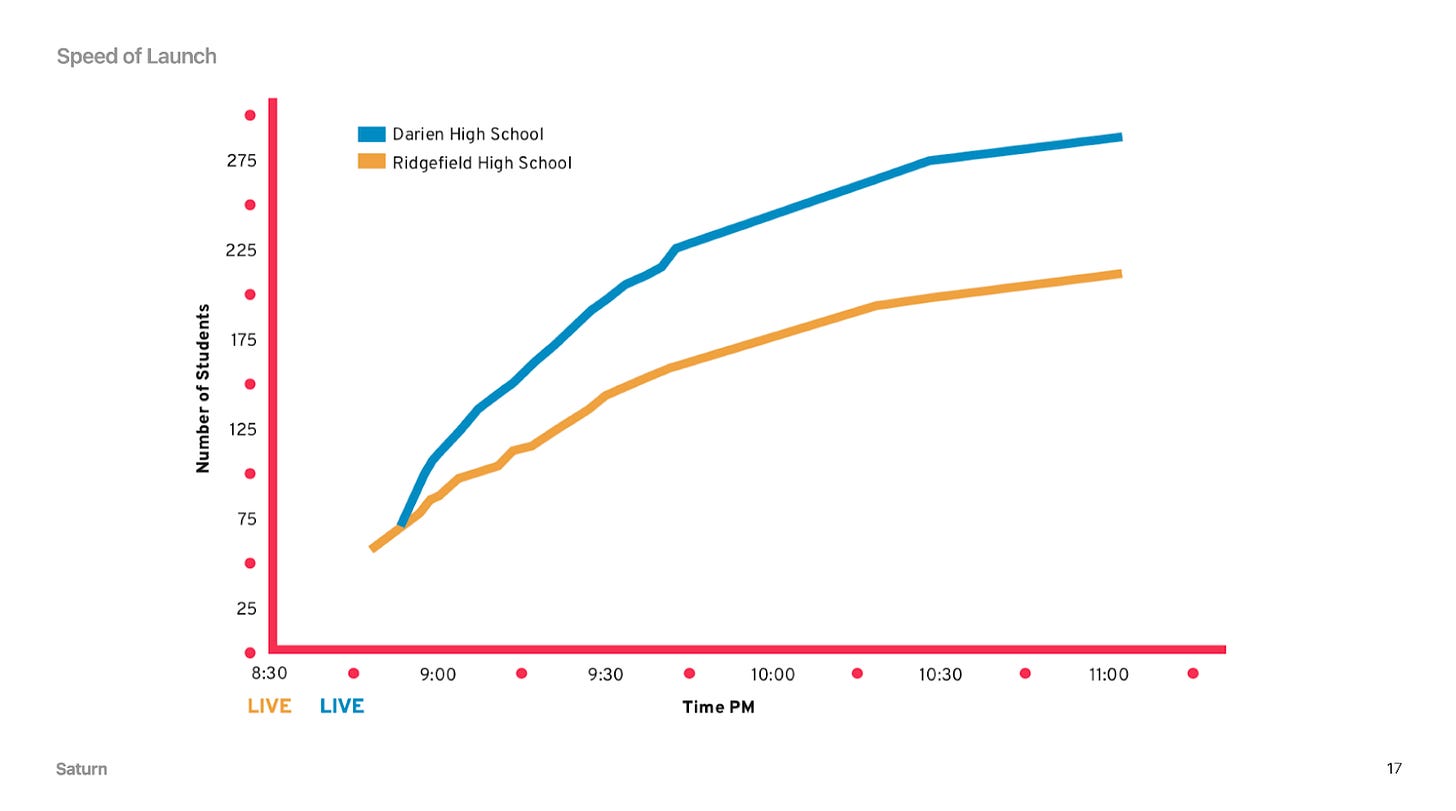
By the time we reached 18 schools, we were balancing the need to ship new features and bug fixes and also launch at new schools. We decided to finally consolidate into a single app: Saturn. By consolidating, we unlocked a significantly faster school launch rate while preserving the personal touches users were loving.
We wanted the experience of joining your school to be magical regardless of our scale. Even today, you arrive, add your classes, and everything is reflected perfectly. It leaves you with a “how did they do that?” feeling. The calendar is what feels the most familiar—it’s your daily schedule, after all. The app is still colorized for your school, and you’re greeted on arrival with your school mascot and friends’ avatars. Delight always matters.
We chose to scale this personalized product approach, instead of changing the product to make it less personal. This now results in bespoke support for our nearly 20,000 schools.
To be clear: we weren’t the first to do this. Facebook, for example, went to significant lengths to support their early schools well, which was fundamental to achieving significant depth in each. This got the network off the ground and eventually allowed them to expand to a broader product.
There are two schools of thought around these kinds of bespoke models:
Avoid silos at all cost, as they will naturally inhibit scale.
Silos enable better product-market fit by solving for users who are very similar, and over time that will help you build a product that remains high-fit across the country.
We are believers in the latter—although this approach requires patience and, if you’d like to scale nationally without compromise (as we did), a willingness to invest heavily in building unique tools and infrastructure and hiring more people. Some founders may not choose to do this or may not be able to raise the capital to support it. We didn’t really have a choice; our product was built around a utility that was complicated to develop and maintain. This forced us to build a larger, more experienced team, capable of handling the operational overhead that would come with growth.
One note: When developing products for small audiences, be careful not to overspecialize for a specific area, community, type of user, etc. For us, this meant a school district, or geography. A good way to avoid this is to use an approach around opposites. If you’re launching urban schools, try suburban schools; if they are predominantly affluent schools, try schools with students from more mixed economic backgrounds, etc. Our first schools were all in southwestern Connecticut, a very affluent region by national standards. In order to ensure the product had fit with students from different backgrounds (and different types of schools), we next launched schools in more economically diverse parts of New Jersey, Massachusetts, etc.
This is especially important if you want to raise venture capital. Investors will always want to know the “bounds” of users you have tested with: across age, income level, region, etc. The more types of users you’ve proven your product can win over, the better.
Takeaway: When users are in your app, they need to feel at home. Much like a personal gift from a friend, building a deeply personal user experience earns user trust and engagement. Always be thinking about the things, big and small, that can make users feel that magic.
3. It’s OK to be unscalable—you can make it scale later
For us, this was not only relevant in the context of building custom apps for each school when we were getting started, but also building a team of local ambassadors to help us win over the students at each school.
Using the calendar as the retentive “backbone” of the product presented a problem. We learned quickly that inaccurate calendars caused user churn, and it was very challenging to maintain accurate ones. Schools have unique schedules and are changing them constantly, for reasons as simple as the weather. A single storm system can cause chaos for millions of students, and our retention was only as good as our ability to maintain accurate data. Without it, users wouldn’t stick around.
There was also no centralized source of data, which made this extremely difficult. To start, we sourced data on these changes from students on the ground, and also gave them responsibilities to help with growth.
Many investors told us this ambassador program was fundamentally unscalable, and while we agreed that it added significant friction, the lessons we extracted from the program, the consistency of the early growth they provided, and the access to our users were so valuable that we grew the network to more than a thousand students anyway. Instead of discarding the program at a few dozen schools, we went deeper, refined it, and adapted our approach. And even when their growth responsibilities were eventually retired, we maintained a cohort from this passionate group and continue to leverage them as an invaluable resource for user research.
Scaling our ambassador count to grow our user base wasn’t pretty, but it worked for years. We were able to iterate through the most challenging constraints of building the program and successfully use it as our default model to launch the majority of our first 1,000 schools.
Our ambassadors were helping us in three ways:
Providing us with the data, context, and information about a schedule necessary to launch a school on Saturn, including keeping us in the loop as schedules changed
Helping to “seed” schools (remember, we have a product that works well even if you’re alone, so the first few users are still really valuable)
Spreading the word and establishing a larger initial cohort of users from which we could grow over time
Eventually, we stopped trying to force scale through ambassadors and instead began to productize each of these responsibilities. It’s worth noting that some things can’t be productized, like the need for users who care enough about your product that they grow it organically through word of mouth.
We began to source our data from users on a waitlist. When we launched our first one in July 2021, more than 100,000 students from 10,000 schools joined in 90 days. This gave us a backlog of the information needed to get more schools live.
We turned to crowdsourcing to help maintain calendars, which was simple once the network hit sufficient scale. Instead of relying on ambassadors to keep a school’s schedule up to date, we could entrust our users with this responsibility and use consensus modeling to provide even more accurate data. In this respect, growth gave us optionality and allowed us to eliminate this dependency. The users’ interest was aligned with ours—if they submitted data, they would have an accurate calendar for themselves. It was a reasonable ask. In our case, overcoming this data challenge wasn’t optional; it was a prerequisite to creating a retentive platform.
With more data on school performance over time, we began to see a very clear trend that schools were growing significantly year over year. This validated our hypothesis that once a school was “seeded,” we could invest in it for the long term and it would eventually become fully saturated. If we could get a school live, it didn’t really matter how we got the first few installs, and it was infeasible to launch tens of thousands of schools with a hand-picked student at each one. Once the schools were live at scale, it unlocked new (less targeted) strategies for the top of our funnel, like performance acquisition.
Scaling this program resulted in a deep familiarity with the operational challenges we’d have to overcome and an understanding of growth at the school level—including how to reach and acquire users at a specific school and how to catalyze the growth flywheel consistently, both of which were critical for us to achieve national scale. In short, this most unscalable part of our business provided the insights and lessons we’ve leveraged since to hit a point where our social product could begin to drive real user value.
Takeaway: An advisor once told us, “Startups exist to do things other companies wouldn’t do—or can’t do.” Be scrappy and have a high tolerance for “pain” at the beginning. It will often unlock key lessons you’ll need to scale.